| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
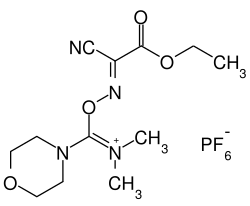
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | COMU | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
(1-Cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethylidenaminooxy)dimethylamino-morpholino-carbenium-hexafluorophosphat | ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C12H19F6N4O4P | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
weißes Pulver[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 428,27 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
COMU [(1-Cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethylidenaminooxy)dimethylamino-morpholino-carbenium-hexafluorophosphat] ist ein Kupplungsreagenz, welches in der Peptidsynthese zur Erzeugung von Peptiden verwendet wird.[2]
Die Verbindung ist thermisch instabil und kann sich stark exotherm zersetzen. Eine DSC-Messung zeigt ab 127 °C eine Zersetzungsreaktion mit einer Reaktionsenthalpie von −736 J·g−1 bzw. −315 kJ·mol−1.[3]
Alternative Kopplungsreagenzien sind z. B. HATU, HBTU, HCTU,[4] TBTU, TOMBU und COMBU.[5]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d Datenblatt COMU® bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 18. Oktober 2016 (PDF).
- ↑ R. Subirós-Funosas, L. Nieto-Rodriguez, K. J. Jensen, F. Albericio: COMU: scope and limitations of the latest innovation in peptide acyl transfer reagents. In: Journal of Peptide Science. Band 19, Nummer 7, Juli 2013, S. 408–414, doi:10.1002/psc.2517, PMID 23712932.
- ↑ J. B. Sperry, C. J. Minteer, JingYa Tao, R. Johnson, R. Duzguner, M. Hawksworth, S. Oke, P. F. Richardson, R. Barnhart, D. R. Bill, R. A. Giusto, J. D. Weaver: Thermal Stability Assessment of Peptide Coupling Reagents Commonly Used in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. In: Organic Process Research & Development. Band 22, 2020, S. 1262–1275, doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00193.
- ↑ C. U. Hjørringgaard, A. Brust, P. F. Alewood: Evaluation of COMU as a coupling reagent for in situ neutralization Boc solid phase peptide synthesis. In: Journal of Peptide Science. Band 18, Nummer 3, März 2012, S. 199–207, doi:10.1002/psc.1438, PMID 22252935.
- ↑ Y. E. Jad, S. N. Khattab, B. G. de la Torre, T. Govender, H. G. Kruger, A. El-Faham, F. Albericio: TOMBU and COMBU as Novel Uronium-type peptide coupling reagents derived from Oxyma-B. In: Molecules. Band 19, Nummer 11, 2014, S. 18953–18965, doi:10.3390/molecules191118953, PMID 25412042.
