Ein Logit ist in der Statistik der natürliche Logarithmus einer Chance, d. h. der Wahrscheinlichkeit geteilt durch die Gegenwahrscheinlichkeit . Unter der Logit-Transformation versteht man die Transformation von Wahrscheinlichkeiten in Logits. Diese wird in der logistischen Regression zur Spezifikation der Kopplungsfunktion verwendet.
Definition
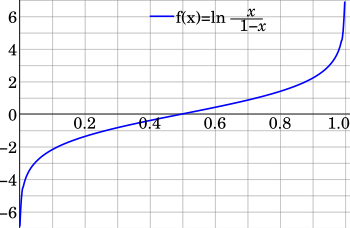
Ein Logit ist der natürliche Logarithmus einer Chance (Wahrscheinlichkeit durch Gegenwahrscheinlichkeit , engl. odds) für eine Wahrscheinlichkeit [1], d. h.
Die Funktion heißt Logit-Funktion. Wenn Wahrscheinlichkeiten in transformiert werden, spricht man auch von einer Logit-Transformation.
Eigenschaften
- Die Logit-Funktion kann auch mit dem Areatangens Hyperbolicus dargestellt werden,
- Es gilt
- Die Logit-Funktion besitzt die Symmetrieeigenschaft
- Die Logit-Funktion ist differenzierbar und hat die Ableitungsfunktion
- Die Logit-Funktion ist invertierbar. Die Umkehrfunktion der Logit-Funktion ist die logistische Funktion (manchmal auch Expit oder Sigmoid genannt):
- .
Anwendung
Die Logit-Funktion kann zur Linearisierung von sigmoiden Kurven verwendet werden und hat daher eine große Bedeutung für die Auswertung von ELISA-Kurven in der Biochemie erlangt.
Die Logit-Transformation ist von zentraler Bedeutung für die logistische Regression.
Siehe auch
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Torsten Becker et al.: Stochastische Risikomodellierung und statistische Methoden. Springer Spektrum, 2016. S. 310.












