| Physikalische Einheit | |
|---|---|
| Einheitenname | Quadratgrad |
| Einheitenzeichen | , , |
| Physikalische Größe | Raumwinkel |
| Formelzeichen | |
| Dimension | |
| In SI-Einheiten | |
Quadratgrad (deg², (°)²) (englisch square degree oder sq degree) ist eine (nicht gesetzliche) Einheit für den Raumwinkel. Anwendung findet sie vor allem in der Astronomie als Maß für die Ausdehnung eines Objekts am Himmel.
Die Untereinheiten heißen entsprechend:
- Quadrat-Bogenminute (englisch square arcmin) Quadratgrad
- Quadrat-Bogensekunde (englisch square arcsec) Quadratminute Quadratgrad.
Der volle Raumwinkel der Himmelskugel beträgt sr =
Die Größe eines Himmelsobjekts in Quadratgrad ergibt sich somit aus dem Anteil der Himmelskugel, den das Objekt bedeckt, multipliziert mit 41253.
Die Umrechnung eines Quadratgrads in Steradiant ergibt sich zu:
bzw.
Für kleine Winkel lässt sich mit Raumwinkeln näherungsweise wie mit Flächen rechnen: ein Objekt, dessen Ausdehnung in einer Richtung 1 Grad misst und senkrecht dazu ebenfalls 1 Grad, bedeckt demzufolge einen Raumwinkel von etwa 1 Quadratgrad.
-
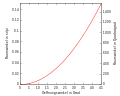
Raumwinkel eines Kegels als Funktion des Öffnungswinkels
-
Vergrößerter Ausschnitt der Funktion für Öffnungswinkel 0–45°